Doublesex(Dsx)最早在黑腹果蝇(Drosophila melanogaste)中发现,是果蝇性别决定级联通路下游的两性基因。该基因与秀丽隐杆线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans)的性别决定基因Maleabnormal-3(Mab-3)及其同源基因均属于Dmrt基因家族(doublesex and Mab-3 related transcription factor),它们编码的蛋白均含有1个保守的DM(double-sex and mab-3)结构域[1-2]。性别决定机制的进化过程十分迅速,但Dmrt家族是个例外,它参与了从无脊椎动物到人类的性别发育,是一个保守性较高的古老的性别调控基因家族。Dsx在昆虫性别决定的整个级联通路中最为保守,因此,Dsx常被作为其他昆虫及昆虫以外的动物性别决定和分化研究的突破口。
甲壳纲动物被认为与昆虫纲动物有着较近的进化关系,昆虫类性别决定机制的研究发现给甲壳动物性别调控相关的研究人员带来了新思路。目前,研究者已对多种甲壳动物的Dsx及同源基因进行了研究。研究者在大型溞(Daphnia magna)中获得了Dmrt93B基因,发现其只在精巢中表达[3];此外,还获得Dsx基因,其中Dsx1已被确定为环境性别决定过程中调控大型溞雄性特征发育的决定基因[4]。在罗氏沼虾(Macrobrachium rosenbergii)中,克隆出了Dmrt11E基因,发现其在精子发生过程中可以定位到精原细胞和精子中[5]。在东方刺龙虾(Sagmariasus verreauxi)中还发现了1个Y连锁的含有DM结构域的基因(iDMY),是常染色体上iDmrt1的删减版本,该基因可能通过显性负效应调控常染色体上iDmrt1基因的功能而发挥性别决定与分化的作用[6]。
克氏原螯虾(Proambaus clarkii),俗名淡水小龙虾,是我国重要的淡水虾类养殖品种。因其独特的风味,较高的营养价值,深受人们的喜爱,被称为夏季消费的“网红”。克氏原螯虾整体产业在我国具有非常重要的经济地位,2018年,全国小龙虾养殖总面积达112万hm2,其主要养殖方式为稻田养殖(84万hm2)和池塘养殖(近20万hm2),养殖总产量达163.87万t,经济总产值达3 690亿元(中国小龙虾产业发展报告https://www.360kuai.com/pc/90bd39d9c1a16c541?cota=3&kuai_so=1&sign=360_57c3bbd1&refer_scene=so_1)。克氏原螯虾单性养殖模式的实现,有助于提高经济效益;同时还可以作为其传播的一道防线,降低养殖过程中逃逸虾在外界环境中泛滥孳生,从一定程度上对生态环境起到保护作用。
性别决定和性别分化机制的了解是实现单性选育的基础。目前,克氏原螯虾性别调控相关基因的研究,除了胰岛素样促雄性腺激素基因(insulin-like androgenic gland hormone gene,IAG)[7]外,未见有其他报道。因此,本研究利用RACE技术从克氏原螯虾中获得了PcDsx cDNA,并利用qRT-PCR检测该基因在成年克氏原螯虾不同组织及早期发育阶段不同时期的表达情况,以期为甲壳动物性别调控机制的研究提供理论基础,为克氏原螯虾的单性选育提供理论和技术指导。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样本收集
试验所用克氏原螯虾来自华中农业大学水产养殖示范基地,养殖水温20~23 ℃。为了解克氏原螯虾Dsx基因的表达特征,采集成年克氏原螯虾(雌、雄)个体的神经、脑、心脏、肝胰腺、肠、触角腺、肌肉、鳃、血细胞、皮肤、性腺等组织,收集克氏原螯虾无节幼体期、蚤状幼体期的受精卵及出膜后1、3、6、13、15、17、23、28、41、48、98、103、109、115 d的克氏原螯虾头胸甲样品(n=5)。所有的样品保存于RNA保存液中,用于后续RNA提取。
1.2 总RNA提取及cDNA合成
取得的RNA组织样品用TRIZol法(QIAGEN,德国)提取总RNA,用Thermoscientific DNase I(RNase-free)试剂盒除去基因组DNA后,按RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit试剂盒(Thermo Fisher Scientific,美国)说明书反转录成cDNA。
1.3 克氏原螯虾PcDsx基因克隆
克氏原螯虾PcDsx基因的cDNA部分序列从笔者所在实验室测得的克氏原螯虾Survey序列中获得[8],利用Primer 5软件设计特异性引物PcDsx F/R,然后,根据获得的cDNA部分序列按照SMARTer© RACE 5′/3′ Kit(TaKaRa,日本)的说明书设计扩增3′和5′端序列的引物,并反转录特异性cDNA模板,扩增PcDsx 3′和5′端序列。以上引物均由武汉擎科创新生物科技有限公司合成,扩增PcDsx cDNA序列所用引物信息详见表1。
表1 实验所用引物信息表
Table 1 Primer used in the experiment

引物名称Primer name引物序列(5' -3')Primer sequence(5'-3')产物长度/bpProduct length用途DescriptionPcDsx FAGTACCCTACCGACTACCCCCATCCPcDsx RTGTCTGTGGCAACTTTGAAATGAGG815克隆 ClonePcDsx5' R1GATTACGCCAAGCTTTCGCTTGCCTTTCTTCTTGGCTTCGPcDsx5' R2GATTACGCCAAGCTTCGGACTGTGTGGATTGTAGCCGTTTGG约500 About 500克隆ClonePcDsx3' F1GATTACGCCAAGCTTCTGGATGAACTGGTGCGGGAGACGTPcDsx3' F2GATTACGCCAAGCTTAGATGATCAACCAGGTGGTGAGGCC约200About 200克隆ClonePcDsx F2CAACAGCACTCATAGCCCACPcDsx R2TCGCTTGCCTTTCTTCTTGG163qRT-PCR18S-RNA FTATACGCTAGTGGAGCTGGAA18S-RNA RGGGGAGGTAGTGACGAAAAAT147qRT-PCR
注:带下划线的序列是按照RACE试剂盒说明书添加的序列。Note:The underlined sequence was added in the primer according to the instructions of the RACE kit.
1.4 生物信息学分析
将测得的序列修剪后进行拼接(DNASTAR Lasergene,USA),拼接后的序列用在线软件 ORFfinder(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/)和Blast (NCBI,https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)分析,用DTU Bioinformatics (http://www.bioinformatics.dtu.dk/)和ExPASy(https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)推导其氨基酸序列,并分析其蛋白分子质量和等电点,通过SMART在线软件(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)预测结构域。用在线软件I-TASSER(https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/I-TASSER/)预测蛋白的三维结构。各物种的同源氨基酸序列来自NCBI,在MEGA 5.1软件上,用clustalW法对各物种Dsx DM结构域氨基酸序列进行比较分析,并用邻接法(NJ)构建系统进化树,各物种Dsx DM结构氨基酸序列如表2所示。
表2 序列比对及建树所用的Dsx/Dmrt氨基酸序列信息
Table 2 The sequences information of Dsx/Dmrt used in sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis

缩写Abbreviation物种Species序列号Accessionnumber基因名GenenameDpDmrt3DaphniapulexEFX89054.1Dmrt3MrDmrt99BMacrobrachiumrosenbergiiAHI47025.1Dmrt99BMrDmrt11EMacrobrachiumrosenbergiiAHI47024.1Dmrt11EDmDmrtDaphnia magnaA0A0P6CC91DmrtPvDmrt1-likePenaeus vannameiXP_027230501.1Dmrt1-likeAvDmrtA1ArmadillidiumvulgareRXG70637.1DmrtA1HsDmrt1Homo sapiensQ9Y5R6Dmrt1DrDmrt1Danio rerioQ71MM5Dmrt1MmuDmrt1Mus musculusQ9QZ59Dmrt1SviDMYSagmariasusverreauxi ARK36623.1iDMYSviDmrt1SagmariasusverreauxiARK36620.1iDmrt1SvDmrt11ESagmariasu verreauxiARK36622.1Dmrt11EEsDmrt-likeEriocheir sinensisADH15934.1Dmrt-likeAfDsx1ArtemiafranciscanaA0A2S0XSU1Doublesex-1SvDsxSagmariasusverreauxiARK36621.1DoublesexPchDsxPenaeus chinensisAFU60552.1DoublesexMmaDsxMoina macrocopaBAM33613.1DoublesexDmeDsxDrosophilamelanogasterAAF54169.1DoublesexPcDsxProcambarus clarkii/Doublesex
1.5 qRT-PCR
通过qRT-PCR检测克氏原螯虾PcDsx的表达情况。反应体系为20 μL,包括F/R引物(10 μmol/L)各0.2 μL、双蒸水8.6 μL、cDNA模板1 μL和SYBR Green(TaKaRa,日本)10 μL。反应程序为:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性15 s 57 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,共40个循环。18S-RNA作为内参基因,用2-ΔΔCt 法计算PcDsx的相对表达量。
1.6 数据分析
试验数据在Microsoft Excel 2016软件上进行统计,所有试验数据均以平均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示,在SPSS 23.0 软件上进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),采用LSD法进行多重比较检验差异显著性,以字母或“*”代表差异显著性(P<0.05),用软件GraphPad Prism 7 作图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 克氏原螯虾PcDsx 基因的克隆
从精巢组织中获得了PcDsx cDNA全长序列(1 584 bp),包括243 bp 5′ UTR、765 bp ORF(编码254 aa)和576 bp 3′ UTR(图1)。该基因的3′ UTR区有2个mRNA快速降解信号(ATTTA),在降解信号之后有1个GT富集和2个“TTTTTT”(图1)。该基因编码的蛋白有254 aa,相对分子质量和等电点分别为28 559.80和6.46,预测的PcDsx蛋白含有1个N-糖基化位点(N78)和1个由55个氨基酸残基组成的DM结构域,其二级结构和三维结构如图2所示。
利用MEGA 5.1软件将表2中所有基因的DM结构域氨基酸进行多重序列比较及进化树分析,结果如图3A和图3B所示。克氏原螯虾PcDsx与南美白对虾(Penaeus vannamei)Dmrt1-like、中国明对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis)PchDsx、东方刺龙虾SvDsx的 DM结构域有5个保守的半胱氨酸残基(C),可以形成一个锌结合位点(CCHC),在进化树中其蛋白也聚为一支,其中PcDsx与SvDsx的同源性最高;而果蝇和丰年虫(Artemia franciscana)的Dsx以及甲壳类、哺乳类Dmrt的DM结构域则有6个保守的半胱氨酸残基(C),可以形成2个锌结合位点(CCHC和HCCC),而其蛋白与PcDsx的同源性也较远(图3B)。
2.2 PcDsx在成年克氏原螯虾各组织中的表达情况
PcDsx在成年雌雄克氏原螯虾不同组织中的表达情况如图4所示,在成年雄性克氏原螯虾中,触角腺中PcDsx表达量最高,其次是食道下神经节、肌肉组织、精巢、心脏,其他各组织PcDsx表达相对较低,尤其在血和皮肤中;在成年雌性克氏原螯虾中,PcDsx表达量最高的组织亦是触角腺,其次是卵巢、肝胰腺、后肠和肌肉。此外,除了食道下神经节、脑、肌肉组织、精巢、心脏和血中的PcDsx表达水平在雌雄个体间不存在差异,其他组织中PcDsx的表达在雌雄个体间均有显著性差异,其中,在雌性的触角腺、卵巢、肝胰腺、前肠、中肠、后肠、鳃和皮肤中表达水平显著性高于雄性组织。

起始密码子(ATG)用红色字体表示,终止密码子(TGA)用红色字体及下方加*表示;mRNA快速降解信号(ATTTA)用黄色表示;GTF富集和TTTTTTT用蓝色表示。预测的N-糖基化位点用绿色斜体字体表示,DM(doublesex DNA-binding motif)结构域用斜体加下滑线表示。The start codon (ATG) was marked with red,and the stop codon (TGA) was marked with red and indicated with “*”. The mRNA rapid degradation signal (ATTTA) was shown in yellow. GT-rich and “TTTTTT” were marked with blue. Predicted N-glycosylated sites were indicated in green italic font. The deduced doublesex DNA-binding motif (DM) sequences were indicated by itlics and underlined.
图1 PcDsx cDNA序列及推导的其氨基酸序列
Fig.1 Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of PcDsx cDNA
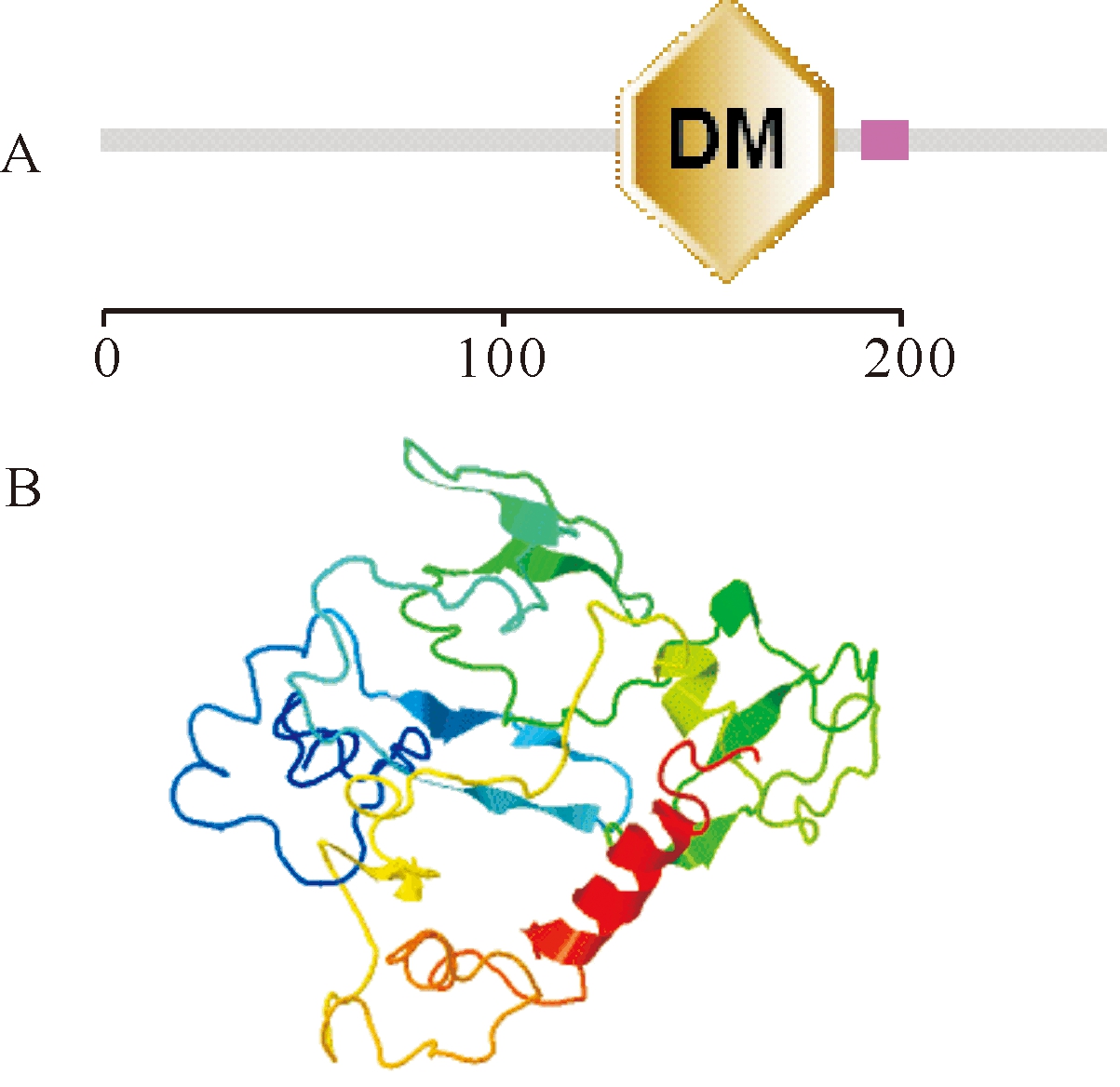
A:预测的PcDsx蛋白结构域。“DM”表示DM结构域,红色区域为低复杂度区域。B:预测的PcDsx蛋白三维结构图。A:The Predicted domains of PcDsx. “DM” indicates doublesex DNA-binding motif,and red box indicates low complexity region. B:The predicred three-dimensiona structure of PcDsx.
图2 预测的PcDsx蛋白结构域及三维结构图
Fig.2 Predicted domains and three-dimensional
structure of PcDsx
2.3 PcDsx在克氏原螯虾早期发育不同时期的表达情况
PcDsx在克氏原螯虾早期发育不同时期的表达情况如图5所示。从无节幼体期开始PcDsx的表达水平逐渐升高,在出膜后1~3 d出现高峰,此后,PcDsx的表达水平逐渐降低,在可以通过外部结构鉴别雌雄(出膜后23 d)后,雌性幼虾中PcDsx的表达水平在出膜后41 d最高,在出膜后98 d次之,而在雄性幼虾中PcDsx表达水平在出膜后115 d 最高,在出膜后109 d次之。有意思的是,在出膜后23 d,雌性幼虾中PcDsx表达水平明显高于雄性,在出膜后41、98、103 d亦是如此;而在出膜后28、48、109 d 和115 d则是雄性幼虾明显高于雌性。

A:Dsx/Dmrt DM结构域的多重比较分析,多序列比较的方法为clustal W法,保守性大于50%的氨基酸残基用彩方形背景突出。B:Dsx/Dmrt DM结构域的进化分析。在MEGA 5.1软件上采用 Neighbor-Joining法构建进化树,bootstrap值设置为1 000次计算重复;克氏原螯虾加红色方框标记。多重比较及建树所用 Dsx或Dmrt相关序列信息见表2。A:Multiple alignment analysis of Dsx/Dmrt DM domains. The alignment was performed by the clustal W algorithm. The identical residue sites in regions with more than 50% conserved level were highlighted with a colored square background. B:Evolutionary analysis of Dsx/Dmrt amino acid sequences. The analysis was constructed by the Neighbor-Joining method with bootstrapping 1 000 replicates,using MEGA 5.1 software. P. clarkii was marked with a red box. The Dsx/Dmrt related information used for multiple alignment and evolutionary analysis were listed in Table 2.
图3 多重比较及进化分析
Fig.3 Multiple alignment and evolutionary analysis
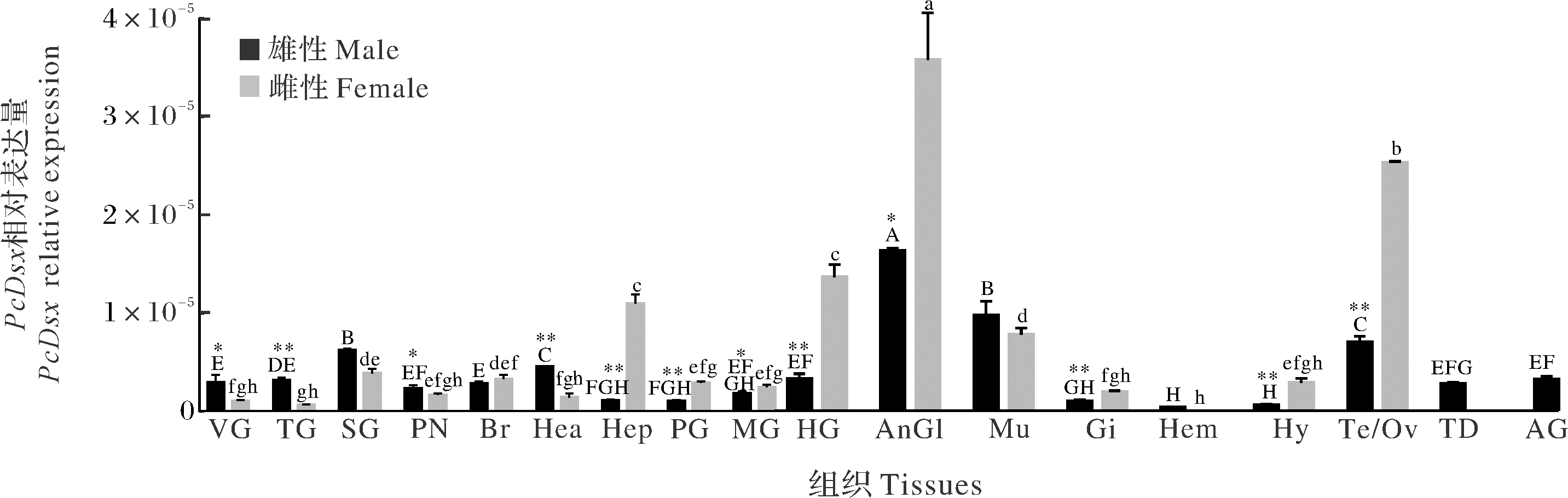
VG:腹部腹神经索 Ventral ganglia;TG:胸部腹神经索 Thoracic ganglia;SG:食道下神经节Subesophageal ganglia;PN:围食道神经 Periesophageal nerve;Br:脑Brain;Hea:心脏Heart;Hep:肝胰腺Hepatopancreas;FG:前肠 Foregut;MG:中肠Midgut;HG:后肠Hindgut;AnGl:触角腺Antennary glands;Mu:肌肉Muscle;Gi:鳃Gill;Hem:血Hemocytes;Hy:皮肤Hypodermis;Te:精巢Testis;Ov:卵巢Ovary;TD:输精管Testicular ducts;AG:促雄性腺Androgenic gland; *: P <0.05;**:P<0.01。PcDsx在成年雄性克氏原螯虾各组织中表达的显著性差异用大写字母表示(P<0.05),PcDsx在成年雌性克氏原螯虾各组织中表达的显著性差异用小写字母表示(P<0.05),PcDsx在雌雄相同组织中表达的显著性差异用星号表示。Different upper-case letters indicated significant differences in the expression levels of PcDsx in different tissues of male P. clarkii (P<0.05). Different lower-case letters indicated significant differences in the expression levels of PcDsx in different tissues of female P. clarkii (P<0.05). Asterisks indicated significant differences in the expression levels of PcDsx between male and female the same tissue.
图4 PcDsx在成年克氏原螯虾组织中的表达模式
Fig.4 Expression pattern of PcDsx in adult P. clarkii
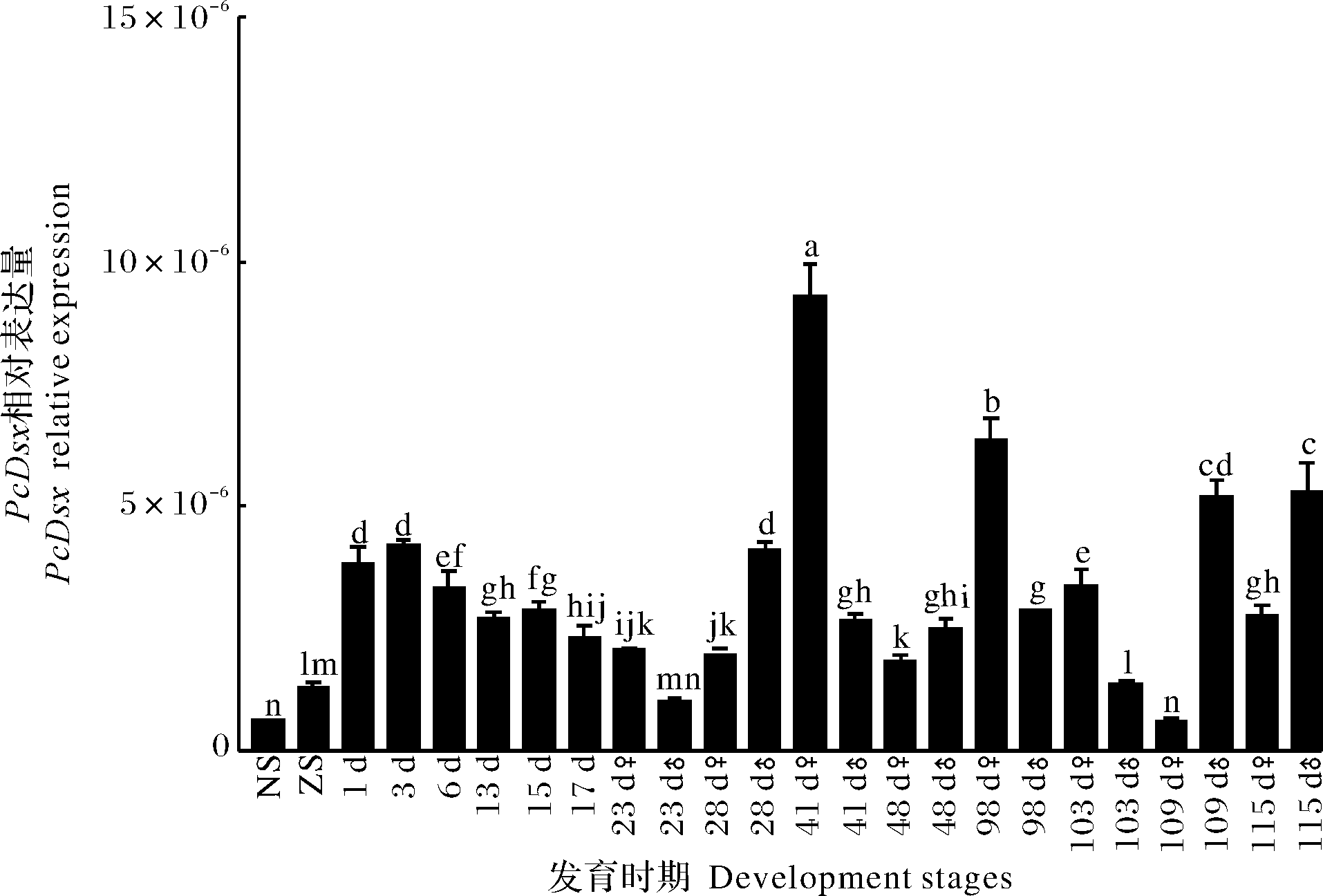
NS:无节幼体期 Nauplius stage; ZS:蚤状幼体期 Zoea stage;1-115 d: 出膜后第1~115天The first-115 days after hatching.
图5 PcDsx在克氏原螯虾早期不同发育时期的表达模式
Fig.5 Expression pattern of PcDsx in the early
development period of P. clarkii
3 讨 论
在本研究中,我们获得了PcDsx cDNA的全长序列,该基因具有Dmrt基因家族的特征,与同源性较高的南美白对虾Dmrt1-like、中国明对虾PchDsx、东方刺龙虾SvDsx的 DM结构域相同,都只含有1个锌结合位点(CCHC),而同源性较远的果蝇和丰年虫的Dsx以及甲壳类和哺乳类Dmrt的DM结构域则含有2个锌结合位点(CCHC和HCCC)。在PcDsx中发现了2个降解信号,降解信号会影响mRNA的稳定性,不知该基因的mRNA的稳定性在雌雄克氏原螯虾间是否有差异,进而影响其在不同性别的克氏原螯虾中的功能。
在东方刺龙虾中,对性发育相关基因SvTKIR和SvDmrt1的研究发现,这2个基因在雌雄未成年虾的触角腺中表达水平均较高,而在成年虾的触角腺中的表达则表现出性别二态性,雌性中的表达水平显著高于雄性[9]。在本研究中,PcDsx在成年雌性克氏原螯虾的触角腺组织中表达水平最高,且表达水平显著高于雄性,笔者所在研究小组在对克氏原螯虾PcSxl的研究中发现,该基因在成年雄虾触角腺组织中表达最高,而在雌性中的表达远低于雄性(数据待发表)。目前,尚无法解释这些基因在触角腺中的性别二态性表达现象。触角腺在虾蟹类中的作用类似于哺乳动物的肾脏,用于调节渗透压和离子平衡以及代谢废弃物如尿液的排泄。有证据表明尿液中混有独特的物质,可以传达社会地位、交配、聚合退敌、协调公共生活及其他社会行为的化学信号[10-12],如若触角腺参与这些信号或者交配信号的调节过程,那么这些基因在触角腺中表现出性别二态性表达也有据可依[9],但目前未见相关报道,尚需进一步深入研究。
在甲壳动物中,有的与昆虫性别决定通路上的基因的同源基因,其表达水平对性别具有偏好性,例如,Sxl多具有偏雄性表达的特点,日本沼虾(M. nipponense)[13]和中华绒蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)[14]如此,南美白对虾中的Sxl-1、Sxl-3、Sxl-5和Sxl-6[15]亦是如此。日本沼虾中Fem-1和Fem-1b[16-17]的表达对性别也具有偏好性。甲壳动物性别调控机制具有复杂多样性,性别偏好性表达现象在不同物种中可能不尽相同,如淡水枝角水溞(D. pulex)中的Tra基因[18]和中国明对虾中的Tra-2基因[19]的表达存在性别二态性,而大型溞中的Tra[20]和斑节对虾(P. monodon)中的Tra-2[21]在雌雄间表达则并无明显差异;本研究中PcDsx在雌性克氏原螯虾的卵巢组织中的表达水平高于雄性精巢,而同源性较高的中国明对虾Dsx以及长牡蛎Dsx则在雄性性腺中高表达 [22-23]。
IAG是目前唯一被证实参与雄性甲壳动物性别分化的关键因子[24-25],其可能与Dsx间存在直接或间接的调节关系。在罗氏沼虾中,Dmrt11E基因的沉默会引起IAG转录水平下调[5],同样的,在中国明对虾中,dsRNA干扰Dsx基因的表达后,也会使IAG基因表达水平下降,并且在IAG启动子区域上预测出了Dsx结合位点,推测Dsx基因可能是IAG基因上游调节基因[22]。根据PcDsx和PcIAG在克氏原螯虾早期发育时期的表达情况分析,推测PcIAG基因在直接或间接接收到PcDsx的调节信号后做出相应的反应,在出膜后1~3 d 表达水平达到最高,进而调控克氏原螯虾的雄性第二性征,在出膜后23 d长出雄性特化的第一游泳足,至于克氏原螯虾性别形成的时间我们无法判断,还有待于深入研究。
[1] BURTIS K C,BAKER B S. Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides[J]. Cell,1989,56(6):997-1010.
[2] ZHU L,WILKEN J,PHILLIPS N B,et al. Sexual dimorphism in diverse metazoans is regulated by a novel class of intertwined zinc fingers[J]. Genes & development,2000,14:1750-1764.
[3] KATO Y,KOBAYASHI K,ODA S,et al. Molecular cloning and sexually dimorphic expression of DM-domain genes in Daphnia magnay[J]. Genomics,2008,91(1):94-101.
[4] KATO Y,KOBAYASHI K,WATANABE H,et al. Environmental sex determination in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia magna:deep conservation of a doublesex gene in the sex-determining pathway[J/OL]. PLoS genetics,2011,7(3):e1001345 [2020-05-18]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21455482. DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001345.
[5] YU Y Q,MA W M,ZENG Q G,et al. Molecular cloning and sexually dimorphic expression of two Dmrt genes in the giant freshwater prawn,Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Agricultural research,2014,3(2):181-191.
[6] CHANDLER J C,FITZGIBBON Q P,SMITH G,et al. Y-linked iDmrt1 paralogue (iDMY) in the eastern spiny lobster,Sagmariasus verreauxi:the first invertebrate sex-linked Dmrt[J]. Developmental biology,2017,430(2):337-345.
[7] SHI L L,YI S K,LI Y H,et al. Genome survey sequencing of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii[J]. Molecular biology reports,2018,45(5):799-806.
[8] SHI L L,HAN S X,FEI J M,et al. Molecular characterization and functional study of insulin-like and rogenic gland hormone gene in the red swamp crayfish,Procambarus clarkii[J/OL]. Genes,2019,10(9):645 [2020-05-18]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31455039. DOI:10.3390/genes10090645.
[9] CHANDLER J C,AIZEN J,FITZGIBBON Q,et al. Applying the power of transcriptomics:understanding male sexual development in decapod crustacea[J]. Integrrative and comparative biology,2016,56(6):1144-1156.
[10] AGGIO J,DERBY C D. Chemical communication in crustaceans[M]. New York:Springer,2011:239-256.
[11] SHABANI S,KAMIO M,DERBY C D. Spiny lobsters use urine-borne olfactory signaling and physical aggressive behaviors to influence social status of conspecifics[J]. Journal of experimental biology,2009,212(15):2464-2474.
[12] THIEL M,BREITHAUPT T. Chemical communication in crustaceans:research challenges for the twenty-first century[M]//BREITHAUPT T,THIEL M. Chemical communication in crustaceans. New York:Springer,2011.
[13] ZHANG Y P,QIAO H,ZHANG W Y,et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of two sex-lethal homolog genes during development in the oriental river prawn,Macrobrachium nipponense[J]. Genetics and molecular research,2013,12(4):4698-4711.
[14] SHEN H S,HU Y C,ZHOU X. Sex-lethal gene of the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis:cDNA cloning,induction by eyestalk ablation,and expression of two splice variants in males and females[J]. Development genes and evolution,2014,224(2):97-105.
[15] LOPEZ-CUADROS I,GARCIA-GASCA A,GOMEZ-ANDURO G,et al. Isolation of the sex-determining gene sex-lethal (Sxl) in Penaeus (Litopenaeus) vannamei (Boone,1931) and characterization of its embryogenic,gametogenic,and tissue-specific expression[J]. Gene,2018,668:33-47.
[16] MA K,LIU Z,LIN J,et al. Molecular characterization of a novel ovary-specific gene fem-1 homolog from the oriental river prawn,Macrobrachium nipponense[J]. Gene,2016,575(2):244-252.
[17] RAHMAN N M A,FU H,QIAO H,et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of Fem1b from oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense[J/OL]. Genetics and molecular research,2016,15(2):gmr7950 [2020-05-18]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27323097. DOI:10.4238/gmr.15027950.
[18] CHEN P,XU S,ZHOU W,et al. Cloning and expression analysis of a transformer gene in Daphnia pulex during different reproduction stages[J]. Animal reproduction science,2014,146(3/4):227-237.
[19] LI S H,LI F H,WEN R,et al. Identification and characterization of the sex-determiner transformer-2 homologue in Chinese shrimp,Fenneropenaeus chinensis[J]. Sexual development,2012,6(5):267-278.
[20] KATO Y,KOBAYASHI K,ODA S,et al. Sequence divergence and expression of a transformer gene in the branchiopod crustacean,Daphnia magna[J]. Genomics,2010,95(3):160-165.
[21] LEELATANAWIT R,SITTIKANKEAW K,YOCAWIBUN P,et al. Identification,characterization and expression of sex-related genes in testes of the giant tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon[J]. Comparative biochemistry and physiology-part A:molecular & integrative physiology,2009,152(1):66-76.
[22] LI S H,LI F H,YU K J,et al. Identification and characterization of a doublesex gene which regulates the expression of insulin-like androgenic gland hormone in Fenneropenaeus chinensis[J]. Gene,2018,649(5):1-7.
[23] 张娜,黄雯,许飞. 长牡蛎(Crassostrea gigas)两个Dmrt家族基因的时空表达[J],海洋与湖沼,2015,46(3):717-724. ZHANG N,HUANG W,XU F,et al. Expression of two Dmrt family genes in the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas[J]. Oceanologia et limnologia sinica,2015,46(3):717-724 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] VENTURA T,MANOR R,AFLALO E D,et al. Temporal silencing of an androgenic gland-specific insulin-like gene affecting phenotypical gender differences and spermatogenesis[J]. Endocrinology,2009,150(3):1278-1286.
[25] 张亚群,王克坚. 甲壳动物促雄腺激素功能、生化和分子结构的研究[J]. 水产科学,2014,33(5):67-72. ZHANG Y Q,WANG K J. A review:current research of function,biochemistry and molecular structure of androgenic gland hormone in crustacean[J]. Fisheries science,2014,33(5):67-72 (in Chinese with English abstract).